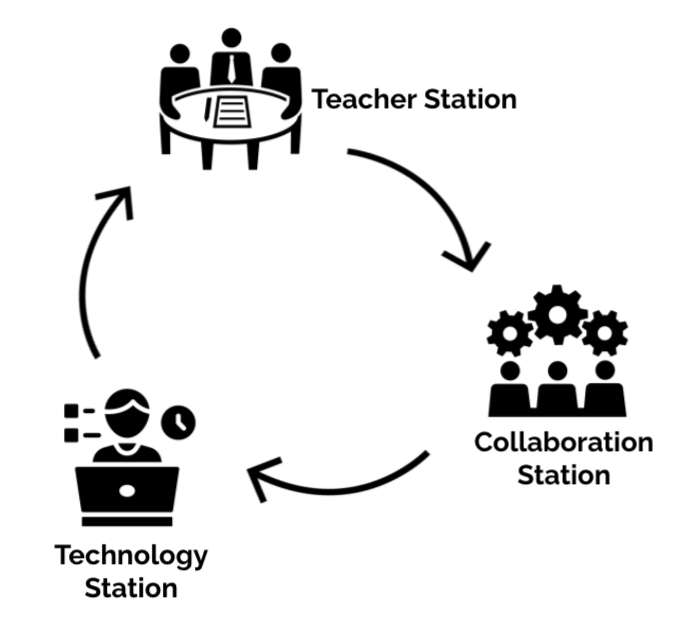
The Station Rotation Progression is a tool that identifies the necessary steps to take when implementing a Blended Station rotation model.
|
Blended Station Rotation Model
Learn more about the Blended Station Rotation Model by visiting the Blended Learning Universe at www.blendedlearning.org. |
|
|
A progression is a pathway a learner might take to reach the end goal or learning target. This tool is carefully sequenced across three phases of implementation:
|
|
Identifies the sequence of teacher and student actions that must be mastered in order to establish the foundation and readiness for an effective station rotation.
|
Identifies the sequence of teacher and student actions that enables differentiation in an effective station rotation.
|
Builds on the Foundation and Differentiated phases to identify the sequence of teacher and student actions that meet the need and interest of every learner.
|
Below you'll find articles, research, practitioner training, and campus or classroom examples from Dallas ISD leaders to suggest the next move you (or for those you coach) might take.
Foundation Phase
Identifies the sequence of teacher and student actions that must be mastered in order to establish the foundation and readiness for an effective station rotation.
Identifies the sequence of teacher and student actions that must be mastered in order to establish the foundation and readiness for an effective station rotation.
Planning Before Lesson
1. Teacher has planned two differentiated small group lessons. |
Varied Learning Experiences [TEI Alignment 1.2, 1.4, 2.4], Differentiated Learning Objectives [TEI Alignment 1.5, 2.1, 2.2], + Data Driven Instruction [TEI Alignment 1.2, 1.4, 2.4] |
Next Move: Review student data to identify two groups of students who need different small group lessons. |
|
2. Teacher creates and shares an agenda for rotations that include student groups, expectations, and transitions. |
Routines + Procedures [TEI Alignment 3.1, 3.2] + Collaborative Grouping [TEI Alignment 1.2, 2.2, 3.3] |
Next Move: Post schedule for rotations and use a timer. Set and practice transition expectations. |
|
Teacher Station
3. Teacher holds students accountable for set expectations for rotations and transitions. |
Routines + Procedures [TEI Alignment 3.1, 3.2] |
Next Move: Directly teach or reset expectations to ensure they are specific, concrete, sequential and observable. |
|
4. Teacher uses small group time to complete one of the three: direct teach, reteach, or address misconceptions based on the trends in data identified in planning. Data Driven Instruction + Differentiated Learning Objectives |
Next Move: Plan two small group lessons that align to the learning objective at the collaboration, and technology station (one standard for all three stations). |
|
5. Teacher checks for understanding and sometimes gives general feedback. Student Feedback + Rapport with Students PBL: Critique & Revision |
Next Move: Create a check for understanding to measure student mastery and give feedback to the group. |
|
Collaboration Station
Next Moves:
|
|
7. Students independently complete tasks aligned to daily class learning objective. Varied Learning Experiences |
Next Move: Plan one activity that aligns to the learning objective at the teacher and technology station (one standard for all three stations). |
|
Next Move: Create a system for students to access an example or provide an answer key to check their work. |
Technology Station
Software makes instructional decisions/Software dominant
9. Students exercise routines and procedures that minimize disruptions. Routines + Procedures |
Next Move: Explicitly teach, practice and post routines for accessing devices and software. |
|
10. Students troubleshoot and access the online task. Routines + Procedures |
Next Move: Create and post a procedure for students to follow when devices aren’t working. |
|
11. Students track progress on software only using metrics of time or lessons completed. Data Driven Instruction |
Next Move: Create a student-facing document to track minutes completed or lessons completed on software. |
|
Differentiated Phase
Identifies the sequence of teacher and student actions that enables differentiation in an effective station rotation.
Identifies the sequence of teacher and student actions that enables differentiation in an effective station rotation.
Teacher Station
1. Teacher has at least three differentiated small group lessons (e.g., mastery, interest, etc.). Data Driven Instruction + Differentiated Learning Objectives |
Next Move: Review student data to identify three groups of students who need different small group lessons. |
|
2. Teacher completes a check for understanding that is specific to the student group. Personalized Learning Pathways |
Next Move: Create a differentiated check for understanding to measure student mastery and give feedback specific to each group. |
|
3. Teacher provides individual, specific feedback (i.e., feedback for learning or aggressive monitoring). Student Feedback PBL: Critique & Revision |
Next Move: Provide students individual feedback on formative assessment and then use a class roster to record the feedback you provide to individual students. |
|
Collaboration Station
4. Students complete tasks that are differentiated [e.g., product, mastery, directions, etc.] and could be completed independently. Differentiated Learning Objectives + Personalized Learning Pathways |
Next Move: Use academic and/or non-academic data when planning to create a differentiated task. |
|
5. Students explain why they’re in a particular group and/or why they are working towards a specific learning objective. Differentiated Learning Objectives |
Next Move:
|
|
6. Students work in partners or groups but not necessarily to create or complete the task. Varied Learning Experiences |
Next Move: Teach and practice expectations for students to work together. (e.g., sentence starters, question prompts, or accountable talk). |
|
Technology Station
Teacher makes instructional decisions/Teacher dominant
Next Move: Create a student-facing document to track progress towards mastery on software programs. |
|
8. Students work on a differentiated tech-based task assigned by the teacher. Personalized Learning Pathways |
Next Move:
|
|
9. Students’ progress and misconceptions are monitored by the teacher in real time. Data Driven Instruction |
Next Move:
|
Personalized Phase
Builds on the Foundation and Differentiated phases to identify the sequence of teacher and student actions that meet the need and interest of every learner.
Builds on the Foundation and Differentiated phases to identify the sequence of teacher and student actions that meet the need and interest of every learner.
Teacher Station
1. Teacher creates and adjusts groups based on student learning needs, real-time adjustments are made as needed. Data Driven Instruction + Collaborative Grouping |
Next Move:
|
|
2. Teacher aligns small group instruction to common standard(s) with differentiated learning objectives for the individual student. Personalized Learning Pathways |
Next Move: Review individual student work and data to create a learning objective aligned to the student’s misconception of the standard. |
|
3. Teacher checks for understanding through a formative assessment that is varied, authentic, relevant, and rigorous. Authentic Assessment |
Next Move: Close out the teacher station by using differentiated formative assessments to measure student mastery. |
|
Collaboration Station
Next Move: Assign and support students in learning the different roles he or she might play in authentic group collaboration. |
|
5. Students co-create products that are authentic and meaningful. Authentic Assessment PBL: Challenge Problem or Question, Authenticity, Public Product, Student Voice & Choice + Sustained Inquiry |
Next Move: Create collaborative activities that simulate real-life situations and issues that connect to students’ communities. |
|
6. Students reflect on their role in group collaboration. Self-Direction + Collaborative Grouping PBL: Reflection + Student Voice & Choice |
Next Move: Provide a tool (i.e., rubric) for students to reflect on group performance, learning, and how their role and actions contributed to the success of the group. |
|
Technology Station
Student makes instructional decisions/Student dominant
7. Students use individual data to determine tasks to complete. Self-Direction + Opportunities for Input PBL: Student Voice & Choice |
Next Move: Teach students how to review their own data and make purposeful decisions about what to practice or which task to complete. |
|
8. Students showcase learning through digital products. Authentic Assessment PBL: Authenticity, Public Product, + Sustained Inquiry |
Next Move: Assign task(s) that require students to show deep understanding through the creation of a final product that connects to the real world. |
|
9. Students interact digitally to provide feedback and make adjustments to products. Data Driven Instruction + Self-Direction PBL: Critique & Revision, Authenticity, + Public Product |
Next Move: Teach or model protocols for students to collaborate and provide feedback to peers when working online to create a joint product. |
|
| Station Rotation Extended Progression (Updated June 2022) | |
| File Size: | 183 kb |
| File Type: | |
| Station Rotation Progression | Foundation Phase | |
| File Size: | 178 kb |
| File Type: | |
| Station Rotation Progression | Differentiated Phase | |
| File Size: | 171 kb |
| File Type: | |
| Station Rotation Progression | Personalized Phase | |
| File Size: | 213 kb |
| File Type: | |